Abstract
Background:
Infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a rare disease with dismal outcome. While outcomes for older children have improved, with event-free survival (EFS) currently above 85%, newly diagnosed infants (<1 year of age) with KMT2A-rearranged ALL have an 1-year EFS of 54.8% (SE 2.3) and a 3-year EFS of 39.6% (SE 2.3) (48% and 23% for medium risk (MR) and high risk (HR) patients, respectively). Ninety percent of all relapses occur during treatment, 66% within one year of diagnosis. Survival after relapse is only 20%. Intensifying chemotherapy with the Interfant06 protocol has not improved the outcome for infant ALL over the last two decades (Pieters et al., JCO 2019), hence there is an urgent need to improve upfront treatment. We studied the safety and efficacy of blinatumomab, a bispecific T-cell engager antibody targeting CD19, in infants with newly diagnosed KMT2A-r ALL.
Methods:
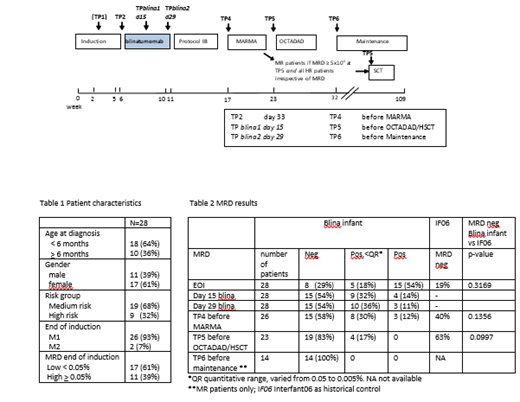
We conducted a prospective, single-arm, international, multicenter, phase 2 study. Newly diagnosed patients <1 year of age with KMT2A-r ALL treated according to the Interfant06 protocol and with a M1/M2 marrow at the end of induction (EOI) were eligible to receive one course of blinatumomab (15ug/m 2/day, 28 day continuous infusion) after induction (Figure 1). Minimal residual disease (MRD) was measured at EOI (TP2), during blinatumomab (TP blina1 day15 and TP blina2 day29), before MARMA (TP4) and OCTADAD/hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) (TP5), and at the start of maintenance (TP6) using MLL and/or Ig/TCR polymerase chain reaction. HR KMT2A-r infant ALL was defined as age <6 months at diagnosis AND white blood cell count≥300x10 9/L and/or poor prednisone response. All other KMT2A-r patients were classified as MR. MR patients with MRD levels >0.05% before OCTADAD and all HR patients in complete remission were eligible for HSCT. (Serious) Adverse Events ((S)AEs) were collected from the start of blinatumomab until the next treatment block. Outcome data were compared to historical controls.
Results:
Twenty-eight patients were enrolled. Baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. The median follow-up was 11 months (range 1.5-33 months). All patients received the full course of blinatumomab without treatment interruptions. Seven SAEs were reported during blinatumomab (3 fever, grade 1 and 4 infections, grade 3-4). None of the patients experienced neurological (S)AEs. In total, 70 AEs were reported, the most frequent grade >3 adverse events were febrile neutropenia (n= 2), anemia (n=5), and elevated GGT (n=2). MRD negative complete response occurred in 54% (n=15/28) at TP blina1, as well as at TP blina2 (after 2 and 4 weeks of blinatumomab, Table 2), which tended to be higher compared to the end of consolidation in Interfant06 (40%, p=0.16). There were 89% (25/28) of patients who were MRD negative or not quantifiable (<0.05%) at TP blina2. None of the MR patients had an indication for HSCT based on high MRD before OCTADAD, compared to 20% in Interfant06, however one patient was transplanted per investigator's discretion. All MR patients who continued chemotherapy became MRD negative during further treatment. MRD negative complete response at the end of blinatumomab was more frequently found in MR compared to HR patients (68% vs 22%, p=0.0418) and in patients with low MRD at EOI (<0.05%) compared to patients with high MRD at EOI (76% vs 18 %, p=0.0056). The 1-year EFS was 96.2% (SE 3.8). One death in first complete remission (CR1) occurred just before HSCT, which was not blinatumomab related (tracheal bleeding due to a tracheal cannula). One MR patient with high MRD at EOI had a combined CD19 positive relapse in the bone marrow and CNS at the end of maintenance, and is in continuous CR2 after HSCT.
Conclusion:
This is the first trial to use blinatumomab in infants with newly diagnosed KMT2A-r ALL. Blinatumomab added to the Interfant06 backbone was very well tolerated, and has promising efficacy in terms of a high rate of complete MRD response and short term EFS. Longer follow-up is awaited, but the low relapse rate after blinatumomab is remarkable, given that in historical controls relapses occur frequently and early, during therapy. Given these findings, blinatumomab will be implemented for all infants with newly diagnosed KMT2A-r ALL in the next Interfant21 protocol.
Nysom: Y-mAbs: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: teaching; EUSA Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: teaching. Biondi: Amgen: Honoraria; Incyte: Consultancy, Other: Advisory Board; Bluebird: Other: Advisory Board; Novartis: Honoraria; Colmmune: Honoraria.
Investigational use of blinatumomab
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract